If key already exists and is a string, this command appends the value at the end of the string. If key does not exist it is created and set as an empty string, so APPEND will be similar to SET in this special case.
Redis Client Commands
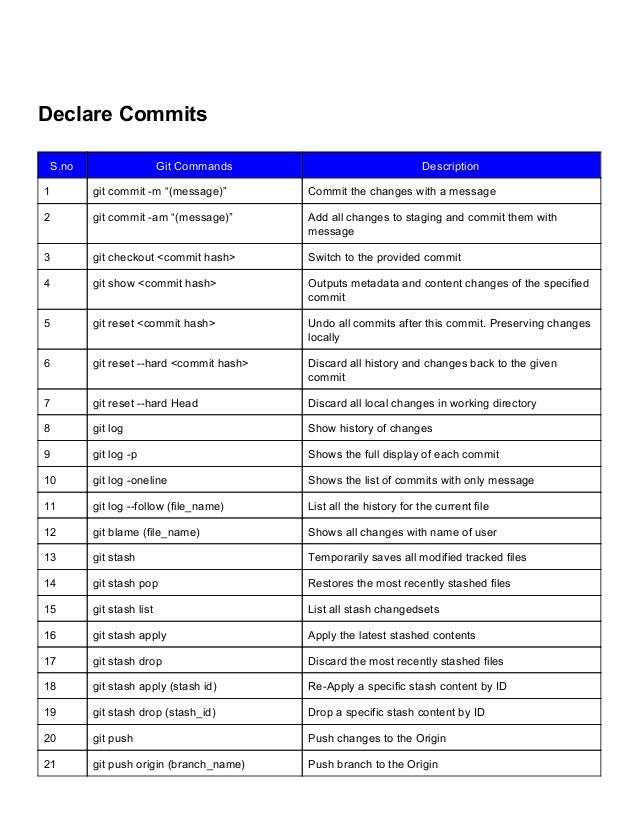
Start redis server on Ubuntu and Mac redis-server; Start redis client redis-cli; Persistence. Redis can fork and then backup to a relational database. Redis can append to a local file with the insert of n configurable keys since last backup file write. Common Redis commands Redis has commands available to work with its data types: Strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps, and hyperloglogs. These are sort of standard commands available in most languages that deal with data structures. REDIS cheatsheet v1.0 starting the server cd redis;./redis-server running the client./redis-cli command exists key Test if specified key exists. Return: 1 if exists, 0 if not commands generic commands for all types del key1 key2. KeyN Remove the specified keys. Return: integer 0 if keys removed, 0 if none of the keys existed type key. Available since 2.0.0. Time complexity: O(1). The amortized time complexity is O(1) assuming the appended value is small and the already present value is of any size, since the dynamic string library used by Redis will double the free space available on every reallocation.
*Return value
Redis Cli Count Keys

Integer reply: the length of the string after the append operation.

*Examples
*Pattern: Time series
The APPEND command can be used to create a very compact representation of a list of fixed-size samples, usually referred as time series. Every time a new sample arrives we can store it using the command
Accessing individual elements in the time series is not hard:
- STRLEN can be used in order to obtain the number of samples.
- GETRANGE allows for random access of elements. If our time series have associated time information we can easily implement a binary search to get range combining GETRANGE with the Lua scripting engine available in Redis 2.6.
- SETRANGE can be used to overwrite an existing time series.
The limitation of this pattern is that we are forced into an append-only mode of operation, there is no way to cut the time series to a given size easily because Redis currently lacks a command able to trim string objects. However the space efficiency of time series stored in this way is remarkable.
Hint: it is possible to switch to a different key based on the current Unix time, in this way it is possible to have just a relatively small amount of samples per key, to avoid dealing with very big keys, and to make this pattern more friendly to be distributed across many Redis instances.
An example sampling the temperature of a sensor using fixed-size strings (using a binary format is better in real implementations).
Related commands
Redis-cli list keys
KEYS – Redis, Warning: consider KEYS as a command that should only be used in production environments with extreme care. Array reply: list of keys matching pattern . Use KEYS command only when the key space is reasonably sized. Cool Tip: Delete all keys from the all databases in Redis! Read more → Get All Keys In Redis. Get all keys using the --scan option: $ redis-cli --scan --pattern '*' List all keys using the KEYS command: $ redis-cli KEYS '*'
Redis command to get all available keys?, Try to look at KEYS command. KEYS * will list all keys stored in redis. EDIT: please note the warning at the top of KEYS documentation page:. The KEYS followed by an asterisk (*) instructs Redis to find all keys in the system. That is why the result displays the model and brand keys that were set up in the previous section. How to Retrieve Specific Existing Redis Keys. The previous section explained how to list all existing Redis keys using the command KEYS followed by the wildcard
How to Get All Keys in Redis, As it turns out, every SET command we issued above created a new, unique key within our Redis database. To get a list of all current keys that exist, simply use % redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 127.0.0.1:6379> RPUSH balls 'cricket_160' (integer) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> RPUSH balls 'football_450' (integer) 2 127.0.0.1:6379> RPUSH balls 'volleyball_270' (integer) 3. We can notice that a successful insertion into the list outputs the new length of the list. However, in most cases, we'll be blind to the data insertion activity.
Redis get
Command reference – Redis, MGET key [key ] Available since 1.0.0. Time complexity: O(N) where N is the Maximum database speed, scalability, and concurrency. Try it free today. Get peak performance in the cloud, on premise, or with Kubernetes
MGET – Redis, 0. The CONFIG GET command is used to read the configuration parameters of a Get the value of key. redis> GET nonexisting (nil) redis> SET mykey 'Hello' 'OK' redis> GET mykey 'Hello' redis> Related commands APPEND
GETSET – Redis, Getting input from other programs. There are two ways you can use redis-cli in order to get the input from other commands (from the standard input, basically) A single Redis item in List or Get Operation. Sku: SKU parameters supplied to the create Redis operation. Sku Family: The SKU family to use. Valid values: (C, P). (C = Basic/Standard, P = Premium). Sku Name: The type of Redis cache to deploy. Valid values: (Basic, Standard, Premium) Tls Version
Redis get values by pattern
SCAN – Redis, If you're looking for a way to find keys in a subset of your keyspace, consider using SCAN or sets. Supported glob-style patterns: h?llo matches hello , hallo and @MarkGravell, would you please clarify why the server.Keys(pattern: 'foo') shouldn't be used if we are using 2.8+ instance of Redis?I read the link/page you refer to but it seems to contradict the advice given at redis.io/commands/scan where it says: 'Since these commands allow for incremental iteration, returning only a small number of elements per call, they can be used in production without
KEYS – Redis, Time complexity: O(N) where N is the number of keys to retrieve. Returns the values of all specified keys. For every key that does not hold a string value or does not Returns all keys matching pattern.. While the time complexity for this operation is O(N), the constant times are fairly low. For example, Redis running on an entry level laptop can scan a 1 million key database in 40 milliseconds.
MGET – Redis, HGETALL returns all fields and values of the hash stored at key, you can't specify a mask: http://redis.io/commands/hgetall. You can call KEYS doc:* to get a list I'm trying to use a pattern to retrieve all keys matching a pattern by Stackexchange.Redis. Code. KEYS *o* c#.net redis stackexchange.redis | this question edited Aug 3 '16 at 7:22 Richard 3,583 3 21 43 asked Aug 16 '14 at 18:12 Amir hossein gholzam 652 10 31 1 Are you aware that you shouldn't (in general) use the KEYS statement in live setups
Redis Basic Commands
Redis get all keys and values
Amazon ElastiCache for Redis, Get 750 Hours of Free Cache.T2Micro Node Usage for 12 Months. Sign Up Today. Yes, you can do print all keys using below bash script, for key in $ (redis-cli -p 6379 keys *); do echo 'Key : '$key' redis-cli -p 6379 GET $key; done. where, 6379 is a port on which redis is running. share. Share a link to this answer.
How to Get All Keys in Redis, For the vast majority of data storage with Redis, data will be stored in a simple key/value pair. This is best shown through the redis-cli (command line interface) Retrieving All Existing Keys. As it turns out, every SET command we issued above created a new, unique key within our Redis database. To get a list of all current keys that exist, simply use the KEYS command: > KEYS * 1) 'title:1' 2) 'title:2' 3) 'title' 4) 'author:2' 5) 'author' 6) 'author:1'.
How to get all keys with their values in redis, There is no native way of doing this. The Redis command documentation contains no native commands for getting the key and value of multiple You can use the method mget to get the values of several keys in one call (returned in the same order as the keys): data = r.mget(['123', '456']) To search for keys following a specific pattern, use the scan method:
Redis cheat sheet
Redis Cheatsheet, Redis Cheatsheet. # All the commands you need to know. redis-server /path/redis.conf # start redis with the related configuration file. redis-cli redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SADD KEY_NAME VALUE1..VALUEN Scard Command. redis 127.0.0.1:6379> SCARD KEY_NAME Sdiff Command. Tags Redis Cheat Sheet
Redis Cheat Sheet, The advantage of redis-cli is that you have a help interface and command line history. CLI Queries. Here is a short list of some basic data extraction commands: Redis Cheat Sheet Edit Cheat Sheet When you encounter a Redis instance and you quickly want to learn about the setup you just need a few simple commands to peak into the setup. Of course it doesn't hurt to look at the official full command documentation, but below is a listing just for sysadmins.
Guides on Using the Commands in Redis Cheat Sheet Part 1 , This is part one of a Redis cheat sheet tutorial series. Redis, an acronym for Remote Directory Server, is an in-memory database that supports Download the Redis Cheat Sheet. 2 Pages. PDF (recommended) PDF (2 pages) Alternative Downloads. PDF (black and white) LaTeX . Created By. tasjaevan. Metadata
Redis count values
AWS ElastiCache for Redis, Sign Up For An Account Today & Start Building Your Database For Free With AWS. I want to get the count of values given the key schema. I have a set in my redis with their keys being: 'sample:key:schema' I want to get total number of values associated with this key. Currently, I do the following and it works
SCAN – Redis, 13. Time complexity: O(1). Returns Integer reply of number of total commands in this Redis server. *Return value. The default COUNT value is 10. When iterating the key space, or a Set, Hash or Sorted Set that is big enough to be represented by a hash table, assuming no MATCHoption is used, the server will usually return countor a bit more than countelements per call. Please check the why SCAN may return all the elements at oncesection later in this document.
COMMAND COUNT – Redis, You can increase the count value by HINCRBY command rather than INCR , so that you can get all count values of the key by HGETALL command. For more *Return value. Integer reply: the number of elements in the specified score range. *Examples. redis> ZADD myzset 1 'one' (integer) 1 redis> ZADD myzset 2 'two'
Redis query
How to get SQL-like Experience with Redis?, One to iterate through the data set by primary key, and two to query based on price. Figure 1. Mapping a table to Redis data structures. With this Numeric filters in query¶ If a field in the schema is defined as NUMERIC, it is possible to either use the FILTER argument in the Redis request or filter with it by specifying filtering rules in the query. The syntax is @field:[{min} {max}] - e.g. @price:[100 200]. A few notes on numeric predicates¶
Secondary indexing with Redis – Redis, However often, especially in caching scenarios, there is the explicit need to store indexed data into Redis in order to speedup common queries which require RediSearch is a source available Full-Text and Secondary Index engine over Redis, developed by Redis Labs.
redis-cli, the Redis command line interface – Redis, system cannot do better than 739 microseconds of worst case latency, so I can expect certain queries to run in a bit less than 1 millisecond from time to time. Redis's basic data types do not support multi-conditional queries, full-text search, etc. Therefore, we have modified the Redis source code and transformed Redis into a database that can be used like SQL data through auxiliary indexes. Ths project homepage is https://oncedb.com OnceDB does not change the data storage structure of Redis.
Redis zset
1.2.5 Sorted sets in Redis, of being able to be accessed by member (like a HASH ), but items can also be accessed by the sorted order and values of the scores. Maximum database speed, scalability, and concurrency. Try it free today. Get peak performance in the cloud, on premise, or with Kubernetes
ZADD – Redis, If the key exists but does not hold a sorted set, an error is returned. The score values should be the string representation of a double precision floating point ZSET is a short name for Redis Sorted Set, a Redis data type documented here. Each key in a sorted set has multiple values inside, associated with a floating value score.
ZRANGE – Redis, Returns the specified range of elements in the sorted set stored at key . The elements are considered to be ordered from the lowest to the highest score. Like Redis HASH es, ZSET s also hold a type of key and value. The keys (called members) are unique, and the values (called scores) are limited to floating-point numbers. ZSET s have the unique property in Redis of being able to be accessed by member (like a HASH), but items can also be accessed by the sorted order and values of the scores.
Redis Commands Cheat Sheet Roblox

Redis Command Cheat Sheet Pdf
More Articles
